Human Respiratory System? Explained.
Human Respiratory system is a part of body which provide a way for breathing and surface for gases exchanges. Body get oxygen through respiratory system. It is divide into two parts-
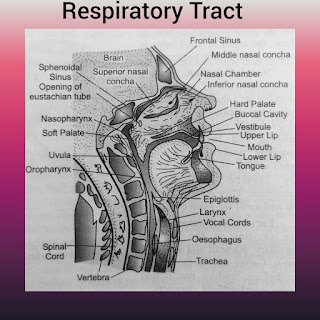
1) Respiratory Tract
2) Respiratory Organ
1) Respiratory Tract- Tract means way. Respiratory tract is a passage way for the fresh air to come inside lungs and foul air to pass away from lungs to environment. It consist nostrils, nasal chamber, internal nares, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles.
i) Nostrils- known as external nares. A pair of slits at the lower end of the nose. They open into the next way that is nasal chamber.
ii) Nasal chamber- It is a pair of passages in the head located above the palate. By nasal septum, both chamber are separate from each other. These chambers shows three regions-
Vestibular Region- It lies just within the external naris. This part is very short and lined with skin. It bear hairs, some sweet and oil glands. The function of hairs is, they did not allow to enter the large dust particle inside the respiratory tract.
Respiratory Region- This is the middle region of nasal chamber. It covered with respiratory epithelium. Mucous and serous cells are present in this region. These mucous cell secrete the viscous fluid called mucus. The serous cells produce the watery fluid. This region act as an air-conditioning.
Olfactory Region- This is the upper region of the nasal chamber. This region lined with olfactory epithelium. This epithelium is confined to the upper part of the nasal chamber and the superior nasal concha. Olfactory region act as organ of smell and help in selecting that which air is good for inspiration.
iii) Internal nares- known as Choanae. This nares open behind into the nasopharynx.
iv) Pharynx- is a part where food and air both passes through it. It is short, vertical, about 12cm long tube behind the buccal cavity. It consist three parts. The upper part known as nasopharynx, the middle part known as oropharynx and the lowest part known as laryngopharynx. The laryngopharynx divide into two tubes Trachea and Esophagus. Trachea tube is for air passage and Esophagus tube for food passage.
v) Larynx- also known as Adam's apple. It is the upper part of trachea. It is short and tubular chamber. Before puberty it is inconspicuous and similar in both sexes. But after puberty it is more prominent in men than in women. It does not allow the food enter inside the trachea. Also, it control the voice so that it called voice box.
vi) Trachea- known as windpipe. It is thin walled tube, about 11cm long and 2.5cm wide. It extends downward through the neck.
vii) Bronchi and bronchioles- Trachea divide into two tubes at the middle of thorax known as primary bronchi. One tube enter into left lung and second tube enter into right lungs. Then these primary bronchi further divide into secondary bronchi and secondary bronchi further subdivide into smaller tertiary bronchi which divide into still smaller bronchioles. Bronchioles are the respiratory tubes, also known as bronchial tree. They are occur only in lungs, their wall consists smooth muscles and they never penetrate to the tissue cells.
Lungs located in the thoracic cavity on the side of the heart. The thoracic cavity is an tight chamber enclosed behind by the thoracic vertebrae. It is closed below by the diaphragm.
Each lung is enclosed with two membrane- visceral pleuron and parietal pleuron. Visceral pleuron are the inner membrane of lungs and parietal pleuron are the outer membrane of lungs. Inner membrane firmly bound to the surface of lungs. Outer membrane held the thoracic wall and the diaphragm by connective tissue. A very narrow space occur between the two pleura is called pleural cavity and it contain the watery fluid called pleural fluid. The pleural cavity is air tight and the pleural fluid lubricate the pleura.
Right lung is larger and heavier, it has 3 lobes. Left lung is smaller and lighter, has 2 lobes.
Inspiration- is also called inhalation. It is an active process in which air moves from outside to inside the lungs. It increase the volume of lungs. The ribs muscle and diaphragm will contract. Because of contraction ribs muscles become upward and forward and Diaphragm become less dome shaped.
Expiration- is called exhalation. It is a passive process in which air moves inside to outside from lungs. It decrease the volume of lungs. During exhalation the ribs muscles and diaphragm will be relaxed. The ribs muscles become inward and backward and diaphragm become more dome like shaped.
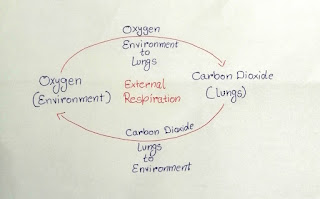
The exchange of gases take place between the blood and alveoli air sac present in lungs. The alveoli contain air (Oxygen) from environment and the blood contain carbon dioxide from body. The blood takes up oxygen from the alveolar air sacs and the alveolar take up carbon dioxide from blood. Blood carry oxygen from lungs to the tissue cells for oxidation and carbon dioxide from the lungs to environment.
It divide into two-
Internal Respiration- In which blood get carbon-dioxide from tissue cells and cells get oxygen from blood.
Disorders of respiratory system- Their are many disorders of respiratory system.
1) Pneumonia- It is a bacterial infection effect the lungs air sacs. Mucus accumulate in the alveoli which cause the inflammation of alveoli. So that alveoli's are not able to get enough air space to support life. The infection leads shortage of breath or severe infection lead to the death.
2) Bronchitis- means the inflammation of bronchi. It is caused by infectious microbes present in the air or cigarette smoking. The bronchial lining swells and produces excess mucus which lead coughing with thick yellow sputum.
3) Hypoxia- It is a condition of oxygen shortage in the tissue. It may be artificial hypoxia or Anemic hypoxia.
Artificial Hypoxia- Shortage of oxygen in the air due to high altitudes like mountains. It cause headache, nausea, vomiting and mental fatigue.
Anemic hypoxia- It is a condition when blood not able to carrying required oxygen due to anemia or carbon monoxide poisoning. It cause shortage of oxygen in blood.
4) Bad Cold- It is chronic obstructive of lungs disease. Caused by air born microbes. These microbes attack on respiratory tract and caused rhinitis, sinusitis, laryngitis and pharyngitis.
Some Important Question-
Q1. Name the respiratory organs of fishes?
Ans. Gills
Q2. Cigarette smoking cause which type of respiratory disorder?
Ans. Bronchitis caused by cigarette smoking.


.jpeg)




.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment